Jean Piaget
Jean Piaget, a pioneering Swiss psychologist, transformed our understanding of cognitive development, proposing distinct stages children's minds progress through as they grow.
Psychologist
August 9, 1896
Leo
September 16, 1980
84
Neuchâtel, Switzerland
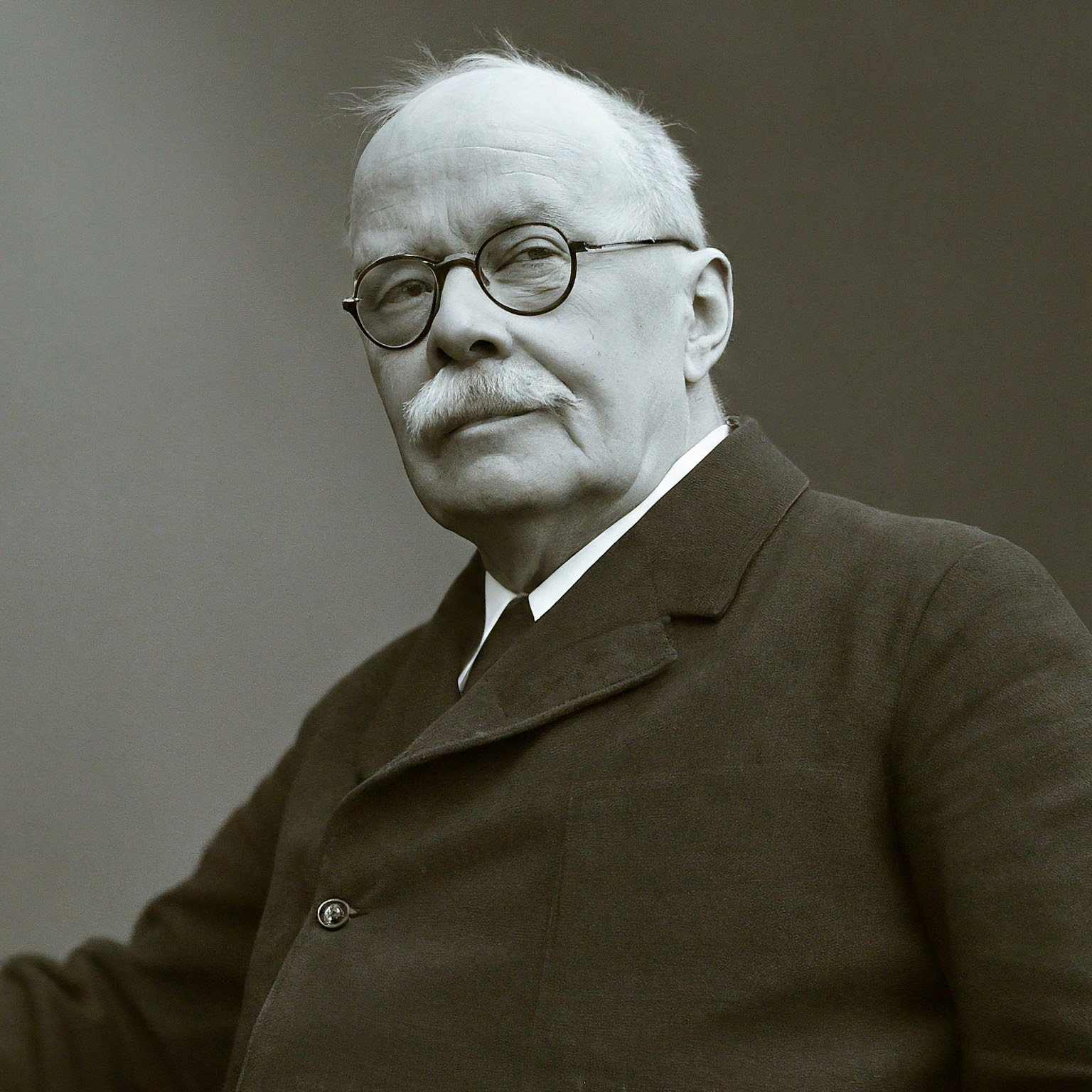
Jean Piaget, a renowned Swiss psychologist, made significant contributions to the field of developmental psychology. His systematic study of children’s cognitive development earned him recognition as a leading figure in 20th-century psychology. Piaget’s most notable work includes his comprehensive theory of cognitive development, often referred to as “genetic epistemology.”
Born on August 9, 1896, in Neuchâtel, Switzerland, Piaget initially pursued studies in zoology and philosophy before venturing into psychology. He trained under renowned psychologists Carl Gustav Jung and Eugen Bleuler in Zurich. Piaget’s early interest in the natural world influenced his approach to understanding children’s cognitive development.
Piaget’s theory of cognitive development proposes that children’s thinking undergoes distinct stages as they grow. These stages include the sensorimotor stage, preoperational stage, concrete operational stage, and formal operational stage. Each stage is characterized by specific cognitive abilities and ways of understanding the world.
Piaget’s research demonstrated that children actively construct their knowledge through interactions with their environment. He emphasized the importance of play and hands-on experiences in promoting cognitive development. His work challenged traditional notions of children as passive recipients of information and highlighted their active role in learning.
Piaget’s contributions extended beyond developmental psychology. He made notable contributions to child psychology, educational psychology, and the study of the origins of knowledge. His insights have influenced various fields, including education, philosophy, and artificial intelligence.
Throughout his illustrious career, Piaget received numerous prestigious awards, including the Balzan Prize, the Erasmus Prize, and the American Psychological Association’s Distinguished Scientific Contribution Award. His work continues to inspire researchers and practitioners in understanding how children develop cognitively and how to foster their intellectual growth.
Jean Piaget’s legacy as a pioneering psychologist endures, and his ideas remain influential in shaping our understanding of human development and cognition.